Webhooks
Intro
Webhooks are notifications sent out by AllTruckJobs when new leads are received. They allow us to send real-time notifications to web applications and reporting systems.
Once webhooks are set up, they send a request to a URL endpoint of your choice. You may set up separate endpoints for each lead event or opt to receive all lead events to the same endpoint.
Currently Supported Formats
- HTTP POST
- JSON
- Basic Authentication
- Bearer Token Authentication
Responding
Your endpoint should return an HTTP status code in the 2xx range to confirm that the data was successfully received. Any status code outside the 2xx range typically means the webhook was unable to complete the requested action.
Common causes for non-2xx response codes include incorrect or invalid URLs on the receiving endpoint, such as typos, or the receiving server rejecting URLs that exceed a certain character length.
Security
Every webhook request includes an X-T5-Signature header that allows you to verify the request originated from AllTruckJobs and that the payload has not been tampered with.
Signature Verification
The signature is generated using HMAC-SHA1 with your API key as the secret. To verify a webhook request:
- Extract the raw JSON body from the incoming request
- Compute an HMAC-SHA1 hash of the body using your API key as the secret
- Base64 encode the resulting hash
- Compare your computed signature with the
X-T5-Signatureheader value
Important Notes:
- Always use a timing-safe comparison function to prevent timing attacks
- The signature is computed from the exact raw JSON body, so do not modify or re-encode the payload before verification
- Verification is optional but strongly recommended for production environments
Error Handling & Retries
Understanding how our platform handles webhook failures will help you design reliable endpoints and troubleshoot delivery issues effectively.
Response Requirements
Any response outside the 2xx range will be treated as a failure and trigger our retry mechanism.
Common Error Scenarios:
Client-Side Errors (4xx)
- 400 Bad Request: Your endpoint rejected the payload format
- 401 Unauthorized: Authentication issues with your webhook credentials
- 403 Forbidden: Your server is refusing the request
- 404 Not Found: Webhook URL is incorrect or endpoint doesn't exist
- 413 Payload Too Large: Your server cannot handle the request size
- 422 Unprocessable Entity: Your server cannot process the webhook data structure
Server-Side Errors (5xx)
- 500 Internal Server Error: Temporary issues with your server
- 502 Bad Gateway: Gateway or proxy server issues
- 503 Service Unavailable: Your server is temporarily overloaded
- 504 Gateway Timeout: Your server took too long to respond
Reference:
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Status
Retries
When a webhook delivery fails (non-2xx response or connection error), AllTruckJobs automatically retries using a set retry schedule:
- Initial attempt: Immediate delivery
- Retry 1: After 1 minute
- Retry 2: After 5 minutes
- Retry 3: After 1 hour
- Retry 4: After 6 hours
- Retry 5: After 24 hours
Total attempts: 6 (1 initial + 5 retries)
After all retries are exhausted, the webhook delivery is marked as permanently failed.
Recommendations When Webhooks Fail:
For 4xx Errors (Client Issues):- Verify your endpoint URL - Ensure the webhook URL is correct and accessible
- Check authentication - Validate that your server can verify the X-T5-Signature header & also confirm that the webhook credentials (or token) are accurate and authenticated
- Review payload handling - Ensure your endpoint can accept JSON payloads and return 2xx responses
- Test URL length limits - Some servers reject URLs that exceed character limits
- Check server error logs - Your server logs may provide insights into the error
- Inspect the .htaccess file - A misconfigured .htaccess file can cause 500 errors
- Contact your hosting provider - They can help investigate server-level issues
- Implement proper error handling - Ensure your endpoint returns 2xx responses for successful processing
- Increase server capacity - Scale your infrastructure to handle webhook volume
- Add monitoring - Track your endpoint's response times and error rates
- Consider queuing - Accept webhooks quickly and process them asynchronously
- Optimize response time - Your endpoint should respond within 30 seconds
- Return success quickly - Accept the webhook and process data asynchronously
- Implement health checks - Monitor your endpoint's availability
- Log webhook attempts - Keep records of incoming webhooks for troubleshooting
- Implement idempotency - Handle duplicate webhook deliveries gracefully
- Use monitoring tools - Set up alerts for webhook failures
- Test regularly - Use our webhook testing feature to verify your endpoint
AllTruckJobs provides comprehensive webhook delivery monitoring:
- Delivery status - Track success/failure for each webhook attempt
- Response codes - See the exact HTTP status codes your endpoint returned
- Response messages - View error details returned by your server
- Retry history - Monitor the complete retry sequence for failed deliveries
- Payload storage - Access request/response data for debugging
Reach out to AllTruckJobs support if you experience:
- Consistently high failure rates (>5%) despite following best practices
- Webhooks failing with valid 2xx responses
- Missing webhook deliveries for confirmed events
- Persistent authentication issues with correct signatures
Lead Events & Payloads
New Lead
*WILL BE DEPRECATED* This event is triggered when you receive a new lead, including real-time leads, unlocked leads, job applicants, and direct applicants. However, it may not capture every event due to candidate windows in effect within our platform. For better coverage, we recommend opting into each specific lead event type listed above instead of relying solely on this event trigger.
Sample POST Payload
{
"event": "new-lead",
"lead": {
"id": 12345,
"first_name": "John",
"last_name": "Doe",
"address": "1234 Example Street",
"address2": null,
"city": "Louisville",
"state": "KY",
"zip": "40210",
"sent": "2015-12-08T15:24:35-05:00",
"email": "johndoe@test.com",
"phone": "+1234567890",
"driver_type": "Student",
"experience": "75",
"endorsement": "Tanker + HAZMAT (X)",
"freight_experience": "Intermodal",
"freight_preferences": "Oil Field",
"license_state": "Idaho",
"preferred_assignments": "LTL",
"preferred_regions": "Midwest",
"has_team": "",
"license_class": "Class B",
"date_of_birth": "11/21/1994",
"twic_card": "No",
"accidents": "4",
"moving_violations": "4",
"last_license_suspension": 2017,
"last_dui": 2017,
"interested_lease_purchase": "Yes",
"teams": "Team",
"trucks_owned": "",
"employment_history": [
{
"company": "Example Company",
"state": "PA",
"phone": "1234567890",
"start_date": "2021-01-01",
"end_date": null
}
],
"job_applications": [
{
"job_id": 39518,
"title": "Example Job Title",
"reference": "EXAMPLE12356",
"is_direct_app": true,
"created_at": "1977-09-20T18:13:10+00:00"
}
],
"is_premium": true
}
}Data Types & Validation
Our webhook mechanism dispatches the following types of events.
Event Types:
| Event Type | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
new-lead
|
DEPRECATED - Generic lead event | Not recommended |
Default event structure:
{
"event": "name-of-event",
"additional-objects": "...varies by event type"
}Here are a few data objects that are commonly used across several event types.
Candidate/Lead Data Fields:
This table outlines the standard data fields for a candidate or lead profile.
| Field | Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
id |
integer | Always present. |
first_name |
string | Always present. |
last_name |
string | Always present. |
address |
string | Always present. |
address2 |
string or null | Secondary address line; Nullable. |
city |
string | Always present. |
state |
string | 2-letter state abbreviation (e.g., "CA"). Always present. |
zip |
string | Always present. |
email |
string | Must be a valid email format. Always present. |
phone |
string | E.164 format (e.g., "+14155552671"). Always present. |
driver_type |
string | Always present. |
experience |
string | Years or level of experience. Always present. |
freight_experience |
array of strings or string | Can be an array or a single comma-separated string. Can be empty array or empty string. |
Job Fields:
| Field | Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
id |
integer | Unique job identifier. Always present. |
title |
string | Job title. Always present. |
driverType |
string | Always present. |
city |
string or null | Job location city. Always present. Potentially Nullable. |
state |
string | 2-letter state abbreviation. Always present. |
zip |
string | Job location postal code. Always present. Potentially Nullable |
payAmountMin |
string | Minimum pay amount formatted as currency string (e.g., "1192.00"). Always present. Can be empty string. |
payAmountMax |
string | Maximum pay amount formatted as currency string (e.g., "1192.00"). Always present. Can be empty string. |
payFrequency |
string or null | Pay frequency (e.g., "Monthly"). Always present. Nullable. |
description |
string | Job description (may contain HTML). Always present. |
requirements |
string or null | Job requirements (may contain HTML). Always present. Nullable. |
isPromoted |
boolean | Whether job is promoted/featured. Always present. |
Employment History Array:
| Field | Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
company |
string | Employer name. Always present. (Max 255 characters) |
state |
string or null | State abbreviation (2 characters). Nullable. |
phone |
string | Contact phone number. Always present. (Max 20 characters) |
start_date |
Date String (YYYY-MM-DD) | Employment start date. Always present. (e.g., "2020-01-15") |
end_date |
Date String (YYYY-MM-DD) or null | Employment end date. Nullable. Null indicates current employment. (e.g., "2023-06-30") |
DateTime Fields & Timezone Information:
- Timestamps: ISO 8601 format with timezone offset. Example:
"2015-12-08T15:24:35-05:00" - Dates: Date only in YYYY-MM-DD format. Example:
"2015-12-08"
Payloads
Next, we'll provide information about the different event type payloads.
New Lead Payload:
Event Structure:
{
"event": "new-lead",
"lead": {}
}Includes all candidate fields plus:
| Field | Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
sent |
ISO8601 date string | Always present. (e.g., "2015-12-08T15:24:35-05:00") |
endorsement |
string | Always present. Can be an empty string. |
freight_preferences |
string | Always present. Can be an empty string. |
preferred_assignments |
string | Always present. Can be an empty string. |
preferred_regions |
string | Always present. Can be an empty string. |
has_team |
string | Always present. Can be an empty string. |
license_class |
string | Always present. |
date_of_birth |
string | Always present. Can be an empty string. (e.g., "02/20/1956") |
twic_card |
string | Always present. Can be an empty string. (e.g., "Yes", "No") |
accidents |
string | Number of accidents. Always present. Can be an empty string. |
moving_violations |
string | Number of moving violations. Always present. Can be an empty string. |
last_license_suspension |
integer or null | Year of last license suspension. Nullable. |
last_dui |
integer or null | Year of last DUI. Nullable. |
interested_lease_purchase |
string | Always present. Can be an empty string. (e.g., "Yes", "No") |
teams |
string | Always present. Can be an empty string. |
trucks_owned |
string | Always present. Can be an empty string. |
is_premium |
boolean or null | |
employment_history |
array of objects | Always present. Can be empty array. |
job_applications |
array of objects | Always present. Can be empty array. |
Mapping Requirements
Mapping our specialty and/or license lists to yours is crucial when building a webhook to ensure data consistency and accuracy. This mapping ensures that the licenses and specialties from our platform align correctly with those in your system, allowing candidates to be properly categorized and routed. Without this mapping, candidates may be added with incomplete data, leading to discrepancies and inefficient lead management.
Below is our current list of specialties and/or license types for mapping. We send the ‘Name’ value with candidate records.
License Types
| ID | Name | Full Name |
|---|---|---|
1 |
Owner Operator | Owner Operator |
2 |
Company Driver | Company Driver |
3 |
Student | Student |
Freight Types
| ID | Name | Full Name |
|---|---|---|
1 |
Dry Van | Dry Van |
2 |
Refrigerated | Refrigerated |
3 |
Tanker | Tanker |
4 |
Dry Bulk | Dry Bulk |
5 |
Flatbed | Flatbed |
6 |
Car Hauler | Car Hauler |
7 |
Oversize Load | Oversize Load |
8 |
Intermodal | Intermodal |
9 |
Box | Box |
10 |
Drop and Hook | Drop and Hook |
11 |
Hopper Bottom | Hopper Bottom |
12 |
Oil Field | Oil Field |
13 |
Yard Spotter | Yard Spotter |
Integration Requirements
| Field | Required | Notes |
|---|---|---|
license_id |
Yes | Must match one of the license IDs above |
Handling Duplicate Candidates
When building webhooks or APIs to receive leads, it's essential to ensure that they are designed to handle duplicate leads—especially those that may already exist in your ATS currently attributed to another vendor.
Please ensure your system checks for existing leads before adding new ones to prevent duplicates. It is essential that existing candidates are upserted with at least the latest referral attribution from our platform, even if other candidate data remains unchanged, to accurately reflect ROI and the effectiveness of our platform.
Key Considerations:
- Check for Duplicates: Use unique identifiers (such as email or phone number) to verify if a candidate already exists in your ATS.
- Update Existing Records: If the candidate is a duplicate, update the existing record with new attribution and candidate data, rather than creating a new entry.
- Maintain Data Integrity: This ensures your candidate data remains accurate, prevents unnecessary duplication in your ATS, and preserves effective attribution for proper evaluation of your lead sources.
Next Steps for Completing Implementation
Once you have configured the webhook, you'll need to set up the endpoint URL in your AllTruckJobs account and link it to the appropriate lead events, as per your setup.
You can either share the webhook endpoint URL with your Client Success Manager or enter it directly into your account. To do this, go to the 'Agency Info' > 'Webhooks' page, then select ‘Add New Webhook.'
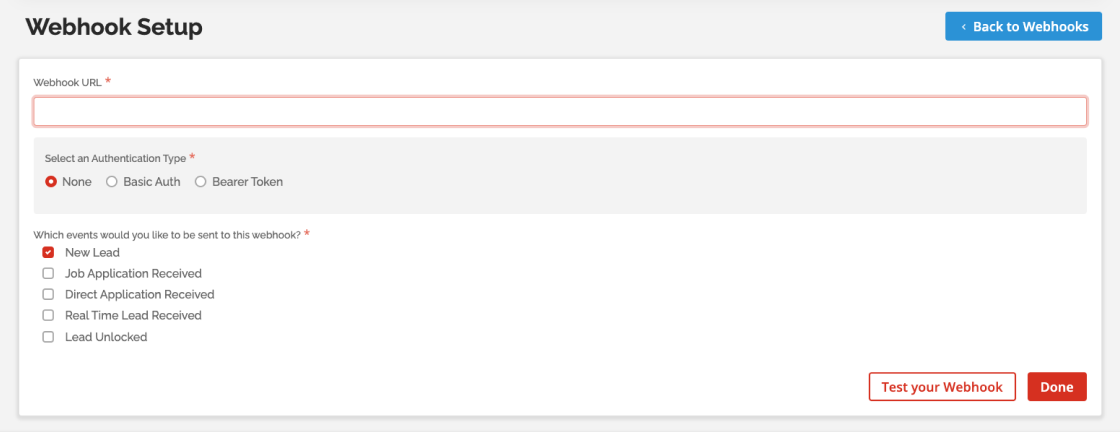
Enter the endpoint URL, choose the correct Authentication Type (as specified in your configuration), and select the new lead event you will be sending to that endpoint.
After entering the details, you can test the webhook to ensure it's functioning correctly. Click on ‘Test your Webhook,' select the new lead event, and click ‘Send Test Event.' The results will appear on the right side of the screen.
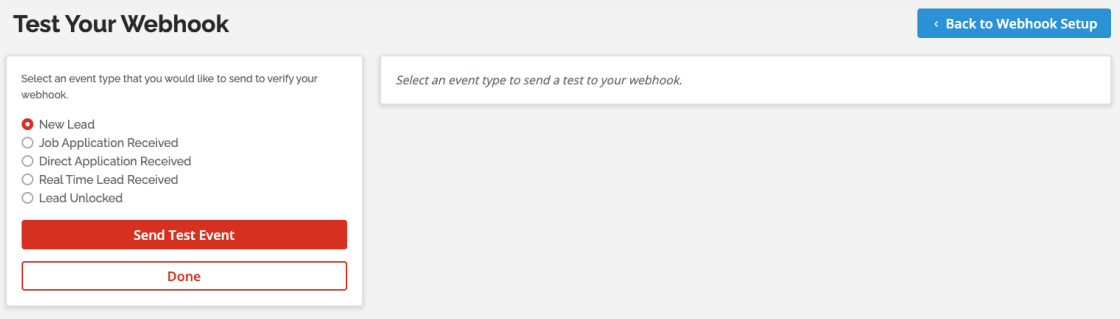
If the tests are successful, you can save the webhook endpoint URL and proceed. You're all set!
